Below is a list of the most commonly requested services we offer. We are constantly adding new tests and new methods for food and environmental microbiology, so if you don't see what you are looking for, please contact us to see if we can help.
Total Plate Count (TPC)
(1-2 days) Total Plate Count determines the number of aerobic bacteria present in a given sample. It is also called the aerobic plate count (APC), standard plate count (SPC), or heterotrophic plate count (HPC). This test is most commonly used to gather information about sanitary quality, process control, and raw ingredients. The values will significantly differ depending on product type.
Anaerobic Plate Count
(2 days) Anaerobic Plate Count determines the number of anaerobic bacteria present in a given sample. The bacteria are grown in a chamber free of oxygen. Anaerobic bacteria are commonly found in soil, the intestinal tracts of animals, and aquatic environments. Although some anaerobic bacteria can be pathogenic, this test is most commonly used to check for potential spoilage organisms.
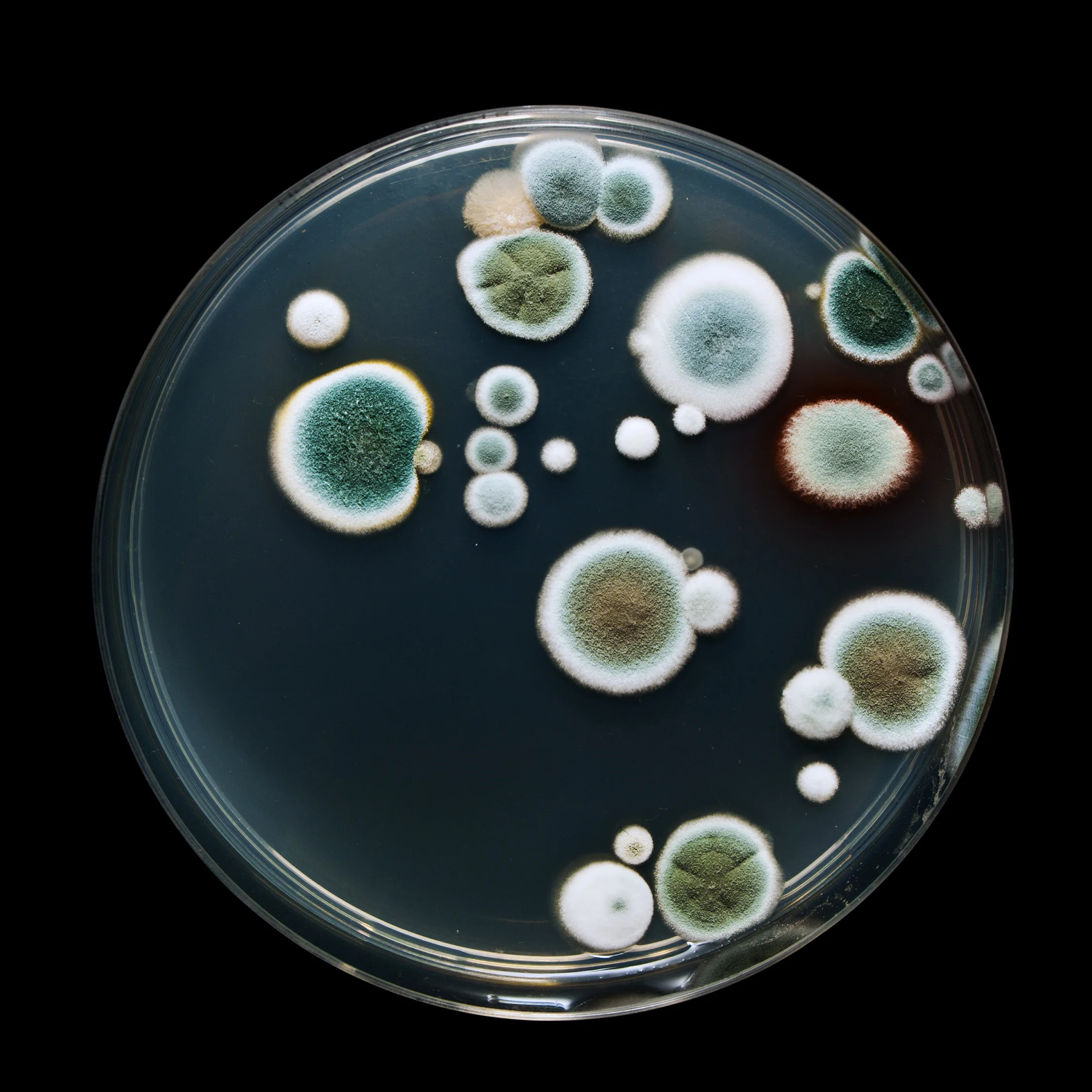
Yeast & Mold Count
(3-5 days) Yeast & Mold Count determines the total number of yeast and the total number of mold in a given sample. Depending on the method these values are combined or reported individually. Yeast and Molds can grow in a wide range of environmental conditions and can cause significant visual and flavor changes to a product. The absence of visual mold does NOT mean that mold is not present; they can be growing internally.
Enterobacteriaceae
(1 day)The Enterobacteriaceae Family are a group of bacteria used as indicator organisms to give information on the overall quality of the food product, the hygienic conditions present during processing, and/or the quality of the sanitation process. _Historically, the family Enterobacteriaceae has been more commonly used in Europe and Asia than in the US as an indicator organism. However, in the past few years, the frequency of Enterobacteriaceae testing in the US has increased. _
Total Coliform
(1-2 days) Coliforms are a group of bacteria classified by growth characteristics and biochemical reactions instead of genetics. They are used as indicator organisms to give information on the overall quality of the food product, the hygienic conditions present during processing, and/or the quality of the sanitation process. Historically, the coliform group has been used as indicator organisms in the United States, whereas the family Enterobacteriaceae has been more commonly used as indicator organisms in Europe.
Total E.coli
(1-4 days) Total E.coli testing determines the total number of generic Escherichia coli (E.coli) present in a given sample with a few exceptions. E.coli O157;H7 and some STEC organisms are not detectable on these generic E.coli tests. E.coli is one of the most common organisms found in the natural flora of the human gut and can be non-pathogenic, however there are also several pathogenic groups of E.coli that are transmitted via food or water.
Coliform/E.coli for Drinking Water
(2-4 days) Coliform/E.coli analysis for drinking water is a presence/absence test. MCL is accredited by the Washington State Department of Ecology for this particular analysis.
Total Staphylococcus (Staph)
(2 days)Total Staphylococcus testing determines the total number of all Staph present in a given sample. Staph is a ubiquitous organism and can easily be found on human skin. Staph testing is often used as an idicator of contamination via human handling of a food product or environmental surface.
Staphylococcus aureus
(2 days)Staphylococcus aureus testing will only determine the number of S. aureus in a given sample. S. aureus produces a heat stable enterotoxin that causes gastroenteritis in humans. S.aureus is highly tolerant to salts and sugars and can also grow with a water activity as low as 0.83.
Coagulase Positive Staphylococcus
(1 day)Coagulase positive Staph are a group of Staph that produce the enzyme coagulase. Most strains of S.aureus are coagulase positive. Some strains of coagulase positive Staph. do produce enterotoxins and some do not.
Salmonella
(1-2 days)Salmonella analysis is a qualitative test (positive/negative) designed to detect all members of the genus Salmonella. The testing is most commonly done with 25 grams, but can also be completed with 375 grams or 750 grams upon customer request. Depending on the strain of Salmonella it can take as little as 1 cell to make someone sick.
Listeria species
(2-3 days)Listeria analysis is a qualitative test (positive/negative) designed to detect all members of the genus Listeria. Listeria testing is most commonly done with 25 grams, but can also be completed with 125 grams upon customer request. Often Listeria species testing is used as an indicator of potential Listeria monocytogenes growth. Environmental swabs are often tested for Listeria species only. Some clients also test their products for Listeria species, whereas others choose to test their products for Listeria monocytogenes only.
Listeria monocytogenes
(2-3 days)Listeria monocytogenes analysis tests for the pathogen only and not the other species of Listeria. Listeria monocytogenes testing is most commonly done with 25 grams, but can also be completed with 125 grams upon customer request. The FDA has a no tolerance policy on Listeria monocytogenes. It is a ubiquitous organism that is known to be quite persistent in food manufacturing environments. Many of the outbreaks of L. mono have occurred because of post-processing contamination of ready-to-eat foods. Furthermore, Listeria is one of the only pathogens that can survive and grow at temperatures as low as 1°C.
E.coli O157:H7
(1-2 days)Escherichia coli 0157:H7 analysis tests for a particular strain(O157:H7) in a group of E.coli known as Enterohemorrhagic E.coli (EHEC). E.coli O157:H7 is not detectable on a generic E.coli test. E.coli O157:H7, which produces shiga toxins, can cause serious illness and has a very low infective dose (10-100 cells).
STEC
(1 day)Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli (STEC) are a group of E.coli that produce Shiga toxins. They are not always detectable on a generic E.coli test. The "big 6" is a reference to the 6 non-O157 serotypes of STEC that are known to be pathogenic: O111, O26, O121, O103, O145, and O45. All of these organisms are part of both the STEC group and the EHEC (Enterohemorrhagic E.coli) group of E.coli, and all can cause serious illness in humans.
Vibrio parahaemolyticus, cholerae, and vulnificus
(1 day)Vibrio analysis tests for three species of Vibrio: parahaemolyticus, cholerae, and vulnificus. This analysis will tell you which of these species is present. All three species are found in marine environments and cause illness in humans.
Bacillus cereus
(1 day)Bacillus cereus testing will determine the number of Bacillus cereus in a given sample. B.cereus can be found in a wide variety of foods, both raw and processed, and can grow under refrigeration temperatures. Illnesses caused by the B.cereus enterotoxin most commonly occur when bacterial populations are greater than 100,000.
Clostridium perfringens
(2 days)Clostridium perfringens testing will determine the number of Clostridium perfringens in a given sample. Clostridium perfingens is an anaerobic organism that produces heat tolerant spores. It takes a high level of bacteria to cause illness (greater than 1 million cells), but C.perfringens has a very fast doubling time. This means it can multiply rapidly and get to a high level of bacteria quickly. Temperature abuse of already cooked food is the most common pathway of C.perfringens pathogenicity.
Lactic Acid Bacteria
(2 days)Lactic Acid Bacteria analysis determines the number of Lactic Acid Bacteria in a given sample. This type of bacteria is categorized by its ability to produce Lactic Acid during fermentation. They are often intentionally used as starter cultures, but they can also cause spoilage in a variety of food products.
Lactobacillus
(3 days)Lactobacillus testing will determine the number of Lactobacillus in a given sample. Lactobacillus bacteria are one genus of the Lactic Acid Bacteria group. They grow very well under anaerobic conditions.
Spore Counts
(2 days) Various test methods can be used to determine the spore count in a given sample. The conditions of these methods change depending on the product; aerobic, anaerobic, mesophilic, thermoduric, acid producing, etc. Contact us for more information.
Water Phase Salt
(1 day - 1wk) Water phase salt is a measurement of the concentration of salt in the water portion of the fish flesh. This analysis includes both moisture testing and salt testing.
Moisture
(1 day - 1wk)Moisture analysis will determine the percentage of moisture in a given sample.
Salt
(1 day - 1wk) Salt analysis will measure the percentage of Salt as NaCl in a given sample.
Water Activity
(1 day) Water activity measures the amount of available water in a given product. This is not the same thing as moisture, as some of the water in a product will be bound by salts, sugars, etc. The water activity of a product can give a good indication of whether or not a product is shelf stable. However, it is important to remember that even with a low water activity bacteria can still be present. The low water activity will prevent bacteria from growing and multiplying, but they can still survive.
pH
(1 day) pH testing measures the acidity or alkalinity in a product. pH testing, along with Water Activity testing, can give a good indication of whether or not a product is shelf stable.
Allergen Testing
(Same Day - 1wk) We currently test both food products and environmental swabs for the below allergens: Milk, Soy, Gluten, Peanut, Egg, and Crustacea. We are capable of testing other allergens upon request. Please contact us with your specific need.
Milk Allergen
(Same Day - 1wk)Total Milk Allergen analysis detects casein and whey proteins from cow, goat, and sheep. The range of quantitation for this test is 2.5 - 25 ppm.
Soy Allergen
(Same Day - 1wk) Soy Allergen analysis detects the presence of soy proteins in food products or on swabs. The range of quantitation for this test is 2.5 - 25ppm. If the possible source of allergen contamination in your samples is from fermentation, or consists of fermented or hydrolyzed materials, current allergen test methods cannot measure allergen levels appropriately in those instances. The result could be an underestimate of the allergen content in the product. Please contact the lab if your sample is of this type.
Gluten Allergen (Gliadin)
(Same Day - 1wk) Gluten Allergen analysis detects Gliadin, one of the major proteins of the Gluten structure found in wheat, barley, rye, and oats. The range of quantitation for this test is 2.5 - 40 ppm. In order for a food product to be labeled as "gluten free" the FDA has set a gluten limit of less than 20 ppm.
Peanut Allergen
(Same Day - 1wk) Peanut Allergen analysis detects peanut protein. The range of quantitation is 2.5-25 ppm.
Egg Allergen
(Same Day - 1wk) Egg Allergen analysis detects processed and unprocessed egg white protein. The range of quantitation is 2.5-25ppm.
Crustacea Allergen
(Same Day - 1wk) Crustacea Allergen analysis detects the presence of crustacea protein from crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, barnacles, etc. The range of quantitation is 2.5-25ppm
FAQ
Does your lab have any certifications?
Yes, we do. We are ISO/IEC 17025:2017 accredited. ISO which stands for the International Organization for Standardization, is considered to be the single most important standard for testing laboratories. In order to become accredited, MCL had to demonstrate technical competence and the ability to produce precise and accurate test results. For a lab to become ISO/IEC 17025:2017 accredited, it does not need to have all of its tests and methods on its scope of accreditation. If a method is not listed on a lab's scope of accreditation, it is not subjected to the rigorous scrutiny of ISO compliance. MCL is proud to have over 95% of our testing methods on our scope of accreditation. We are also accredited by the State of Washington Department of Ecology for Coliform and E.coli analysis in drinking water.
When will my results be ready?
The answer to this question varies greatly depending on a few factors. First, every test has a different turnaround time. Most microbiological tests take at least 24 hours and some can take up to 5 days. Depending on which method is used for your product type, the turnaround time can vary as well. If you look at our services list, you can see the possible ranges for turnaround times for each test we offer. If turnaround time is of utmost importance to you, call us with your specific needs and we will see if our methodology will be a good fit for you. For most all of the microbiological analyses that we offer, we will start the testing the same day that we receive the sample, as long as we receive it before noon.
How do I submit a sample?
For all necessary details on submitting samples, please start here.